|
| Section 1 - Pharmacokinetic Concepts |
The basic goal of therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is to enhance the patient's chance of maximum benefit from a prescribed drug while minimizing the risks of toxicity. Characteristics of drugs associated with TDM are:
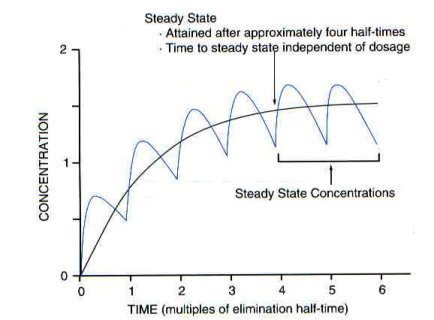
Steady state
As successive doses are administered, drug begins to accumulate in the body.
With first order elimination, at a certain point in therapy, the amount of
drug administered during a dosing interval exactly replaces the amount of drug
excreted (rate in = rate out). When this equilibrium occurs, the peak and
trough drug concentrations are the same for each additional dose given. When
peak and trough concentrations are the same with two or more successive doses,
steady-state is reached.
The time required to reach steady-state is approximately 4 to 5 half-lives.
![]()
You should note from this graph that failure to evaluate steady-state
levels can lead to significant errors in estimates of elimination rate
and in prediction of the appropriate dosage. Therefore, serum sampling
is best performed at steady-state.
Timing serum level draws
Serum samples must be drawn during the elimination phase, when net
distribution is complete.

![]()
You should note from this graph that failure to consider the distribution
phase can lead to significant errors in estimates of elimination rate.
An accurate measure of Kel can only be obtained when serum levels are drawn
in the elimination phase.
Infusion length
Please be aware of the widespread policy of nursing personnel to record a dose
as having been given exactly as ordered if it is given within 30 minutes of the
recorded time. This will lead to significant errors in analysis, therefore,
you must confirm all times, including infusion times.
The length of infusion has a significant effect upon the peak serum level.
If we were to administer the same dose to the same patient at different
infusion rates, the peak levels would differ significantly:
Infusion
Dose
Interval
Peak level
30 min
500 mg
8 hrs
26.8
60 min
500 mg
8 hrs
25.3
120 min
500 mg
8 hrs
22.5
![]()
You should note from this table that failure to use the actual infusion time
can lead to significant errors in estimates of Vd and elimination rate.
Other TDM Precautions
Always rule out errors before accepting out of range data. Common pitfalls and
potential sources of error (in decreasing order of likelihood) are:
KinPlot
To help visualize these pharmacokinetic concepts, I've created a little program
called KinPlot. You enter the model parameters and dosage regimen and the program
displays the resulting serum level plot. You may compare up to six different dosing
regimens on one screen, varying the dose, interval, infusion time and starting
level so that you can how these affect serum levels.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Section 1 - Pharmacokinetic Concepts
www.rxkinetics.com
©Copyright 1984 - 2022, All rights reserved.
RxKinetics, Plattsburg, MO 64477